If a company generates a higher ROA, that company is considered more efficient at turning its investments into profit. Return on assets (ROA) is an important metric for gauging the profitability of a company. However, it is not the only relevant metric, and investors should make sure to look at the full picture when they compare different companies. Most analysts use the total average assets in their calculation rather than the total assets held when net income is recorded because corporate assets can fluctuate over time. Using the average is an attempt to smooth out these fluctuations to get a more accurate picture of a company’s total asset base.
- Some examples of assets are total cash balance, accounts receivable, inventory, PP&E (property, plant, and equipment), investments, and intangible assets (like intellectual property).
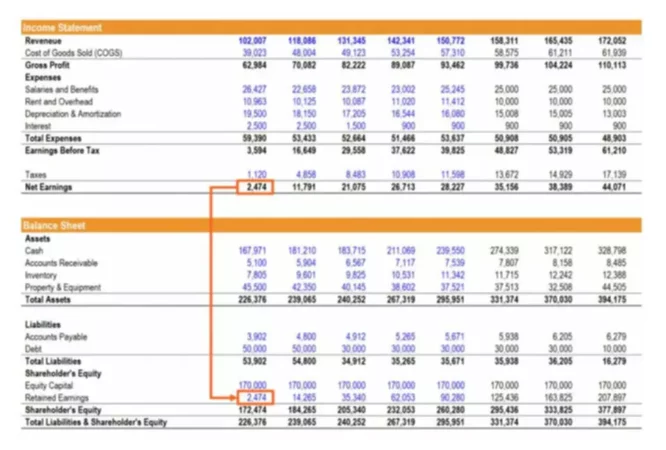
- The increase in PP&E sitting on the B/S can be interpreted as increased CapEx spending, which is often caused by lackluster growth and/or increased competition in the market.
- Average total assets can be calculated by adding the prior period’s ending total assets to the current period’s ending total assets and dividing the result by two.
- She is the author of four books, including End Financial Stress Now and The Five Years Before You Retire.
- Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible.
What does ROA stand for?
The return on assets of a company can also be useful in determining if a stock is undervalued enough to qualify as a value stock. Return on Assets (ROA) is a type of return on investment (ROI) metric that measures the profitability of a business in relation to its total assets. This ratio indicates how well a company is performing by comparing the profit (net income) it’s generating to the capital it’s invested in assets. The higher the return, the more productive and efficient management is in utilizing economic resources. Although there are multiple formulas, return on assets (ROA) is usually calculated by dividing a company’s net income by the average total assets.
Accounting for Medical Practices: Tips and Best Practices
Next, they check their income statement and see they recorded $50,000 in profit for the year. Both ROA and return on equity (ROE) measure how well a company utilizes its resources. But one of the key differences between the two is how they each treat a company’s debt. After all, its total assets include any capital it borrows to run its operations. The ROA formula is an important ratio in analyzing a company’s profitability.
Return on Assets (ROA) vs. Return on Equity (ROE)
In closing, the return on assets (ROA) metric is a practical method for investors to grasp a better understanding of how efficient a company is at converting its asset purchases into net income. To reiterate from earlier, the higher a company’s ROA, the more operationally efficient management is at generating more profits with fewer investments (and vice versa). For the return on assets (ROA) metric to be useful in comparisons, the companies must be in the same (or similar) sector, as industry averages vary significantly. An ROA of 5% or better is typically considered good, while 20% or better is considered great. In general, the higher the ROA, the more efficient the company is at generating profits. However, any one company’s ROA must be considered in the context of its competitors in the same industry and sector.
Understanding Return On Assets (ROA)
The increase in PP&E sitting on the B/S can be interpreted as increased CapEx spending, which is often caused by lackluster growth and/or increased competition in the market. For the “Total Assets” line item, the balance increases from $270m in Year 1 to $278m in Year 5. Under the same time horizon, the “Total Assets” balance decreases from $270m to $262m. But besides comparisons to industry competitors, another use case of tracking ROA is for tracking changes in performance year-over-year. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise. Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible.
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
It is commonly expressed as a percentage using a company’s net income and average assets. ROA can be used by corporate managers, analysts, and investors to figure out how efficiently a company uses its assets to generate a profit. In other words, the return on assets ratio or ROA measures how efficiently a company can manage its assets to produce profits during a period. This can make it helpful to look at the return on total assets ratio formula rather than the revenue formula, particularly when looking for growth stocks. In some industries, this may allow you to get in earlier with companies with a lower initial stock price and a great business model.
This figure tells investors that, when compared to UnitedHealthcare, The Cigna Group may be less efficient at using its held resources to generate profit. The return on assets ratio formula is calculated by dividing net income by average total assets. The purpose of return on assets is to understand the profit a business generates as a percentage of its total assets.
A falling ROA indicates the company might have over-invested in assets that have failed to produce revenue growth, a sign the company may be in some trouble. ROA can also be used to make apples-to-apples comparisons across companies in the same sector or industry. For example, banks tend to have a large number of total assets in the form of loans and investments. A large bank might have $2 trillion in assets and generate similar net income to an unrelated company in another industry. Although the bank’s net income might be similar and have high-quality assets, its ROA might be lower than the unrelated company. The larger total asset figure must be divided into the net income, creating a lower ROA for the bank.
Remember to use total average assets in your calculation, rather than the assets the company held directly when the net income was recorded. The average assets held is calculated by adding the amount of assets a company had at the beginning of the measuring period with the total assets at the end, then dividing by two. It only makes sense that a higher ratio is more favorable to investors because it shows that the company is more effectively managing its assets to produce greater amounts of net income.

Banks, for example, have far fewer capital intensive assets than construction companies because they will invest primarily in intangible assets. This can make ROA a more important factor in industries that are more likely to need to invest heavily in capital assets as a nature of the industry. After investing in a company, monitor how its ROA is changing over time to ensure it can maintain its competitive edge.
ROA should be used in conjunction with other financial ratios, such as ROE and profit margin, for a better indication of performance efficiency. Since ROA shows how efficiently a company is utilizing its assets to generate earnings, ROA can be used for comparison purposes of the same industry. It gives an idea as to how efficient the management is at using its assets to generate earnings. Return on assets indicates the amount of money earned per dollar of assets.
Emily Guy Birken is a former educator, lifelong money nerd, and a Plutus Award-winning freelance writer who specializes in the scientific research behind irrational money behaviors. Her background in education allows her to make complex financial topics relatable and easily understood by the layperson. She is the author of four books, including End Financial Stress Now and The Five Years Before You Retire. A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Finance Strategists has an advertising relationship with some of the companies included on this website. We may earn a commission when you click on a link or make a purchase through the links on our site.
The ROA figure gives investors an idea of how effective the company is in converting the money it invests into net income. The higher the ROA number, the better because the company is able to earn more money with a smaller investment. For example, an auto manufacturer with huge facilities and specialized equipment might have a ROA of 4%. On the other hand, a software company that sells downloadable programs that generates the same profit but with fewer assets might have a ROA of 18%.
A typical ROA will vary depending on the size and industry that a company operates in. Be careful when comparing the ROAs of two companies in different industries. Read on to learn how to calculate return on assets from the ROA formula and how these numbers can be useful for investors. For instance, the cash balance is increasing, which means the company has more liquidity on hand and fewer cash outflows related to inventory purchases and Capex. To reiterate from earlier, the equation for calculating the return on assets is shown below. Regarding the fixed assets base (i.e. the PP&E), the decline of $16m implies fewer capital expenditures are required.
However, in the “Downside Case”, the company’s return on assets (ROA) declines from 8.5% in Year 1 down to 6.1% – with the opposite changes (and implications) on the balance sheet and income statement. But if those companies were to raise debt capital, their ROE would rise above their ROA from the increased cash balance, as total assets would rise while equity decreases. Since ROA is expressed in percentage, the result of dividing the net profit by the average total assets should be multiplied by 100. Industries that are capital-intensive and require a high value of fixed assets for operations, will generally have a lower ROA, as their large asset base will increase the denominator of the formula.

