
It is an entry that increases an asset account or decreases a liability account. In the double-entry accounting system, transactions are recorded in terms of debits and credits. Since a debit in one account offsets a credit in another, the sum of all debits must equal the sum of all credits. Double-entry bookkeeping is an accounting method where each transaction is recorded in 2 or more accounts using debits and credits. A debit is made in at least one account and a credit is made in at least one other account. Every modern accounting system is built on the double entry bookkeeping concept because every business transaction affects at least two different accounts.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
That’s it—each financial transaction has just one line, and you don’t make multiple entries in multiple accounts. It is not used in daybooks (journals), which normally do not form part of the nominal ledger system. Give your skills a boost with Intuit Academy Bookkeeping Professional Certificate. You’ll learn bookkeeping basics like double-entry accounting, along with accounting for assets and financial statement analysis.
Contents
Essentially, the representation equates all uses of capital (assets) to all sources of capital (where debt capital leads to liabilities and equity capital leads to shareholders’ equity). For a company to keep accurate accounts, every business transaction will be represented in at least two of the accounts. This is always the case except for when a business transaction only affects one side of the accounting equation.
Getting Your Small Business Out of Debt

Whether one uses a debit or credit to increase or decrease an account depends on the normal balance of the account. Assets, Expenses, and Drawings accounts (on the left side of the equation) have a normal balance of debit. Liability, Revenue, and Capital accounts (on the right side of the equation) have a normal balance of credit.
- If a company has $100 in assets and $110 in liabilities, then its equity would be -$10.
- A bachelor’s degree in accounting can provide you with the necessary skills to start an entry-level role as an accountant.
- Each transaction is recorded in at least two different accounts, with one account debited and another credited.
- In accounting, a debit refers to an entry on the left side of an account ledger, and credit refers to an entry on the right side of an account ledger.
- Double entry accounting, also called double entry bookkeeping, is the accounting system that requires every business transaction or event to be recorded in at least two accounts.
This system is similar to tracking your expenses using pen and paper or Excel. When all the accounts in a company’s books have been balanced, the result is a zero balance in each account. The term “double entry” has nothing to do with the number of entries made in a business account. For every transaction there is an increase (or decrease) in one side of an account and an equal decrease (or increase) in the other.
What is the double-entry bookkeeping system?
For example, an e-commerce company buys $1,000 worth of inventory on credit. Assets (the inventory account) increase by $1,000 and liabilities (accounts payable) increase by $1,000. Nowadays, the double-entry system of accounting is used all over the world.
For instance, if you sell inventory, you’ll have an inventory account, which is a type of asset account. And if you hire employees, you’ll need a wages account, which is a type of expense account. Because the accounts are set up to check each transaction to be sure it balances out, errors will be flagged to accountants quickly, before the error produces subsequent errors in a domino effect. Additionally, the nature of the account structure makes it easier to trace back through entries to find out where an error originated. The total amount of the transactions in each case must balance out, ensuring that all dollars are accounted for.
In fact, a double-entry bookkeeping system is essential to any company with more than one employee or that has inventory, debts, or several accounts. Let’s look at some examples of how double-entry bookkeeping is used for some common accounting transactions. So, if assets increase, liabilities must also increase so that both sides of the equation balance. The bank’s records are a mirror image of your records, so credit for the bank is a debit for you, and vice versa. This system of accounting is named the double-entry system because every transaction has two aspects, both of which are recorded. Credits add money to accounts, while debits withdraw money from accounts.
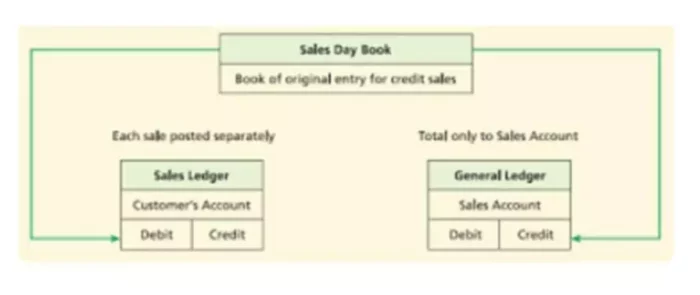
A second popular mnemonic is DEA-LER, where DEA represents Dividend, Expenses, Assets for Debit increases, and Liabilities, Equity, Revenue for Credit increases. However, as can be seen from the examples of daybooks shown below, it is still necessary to check, within each daybook, that the postings from the daybook balance. Learners are advised to conduct additional research to ensure that courses and other credentials pursued meet their personal, professional, and financial goals. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology.
Bookkeeping and accounting are ways of measuring, recording, and communicating a firm’s financial information. A business transaction is an economic event that is recorded for accounting/bookkeeping purposes. In general terms, it is a business interaction between economic entities, such as customers and businesses or vendors and businesses. Remember that example where you bought $5,000 of equipment for your business?
Obviously, single-entry accounting is much simpler than double-entry, but it’s also much less accurate. And since it doesn’t break down your cash flow into categories like expenses, assets, and equity, single-entry bookkeeping can’t give you any real insight into your business’s performance. Double-entry bookkeeping is the process of recording two entries—a credit and a debit entry—for every one financial transaction. This equation means that the total value of a company’s assets must equal the sum of its liabilities and equity.
The 15th-century Franciscan Friar Luca Pacioli is often credited with being the first to write about modern accounting methods like double-entry accounting. He was simply the first to describe the accounting methods that were already common practice among merchants in Venice. If the bakery’s purchase was made with cash, a credit would be made to cash and a debit to asset, still resulting in a balance.
She credits her technology expense account for $1,000 and debits her cash account for $1,000. This is because her technology expense assets are now worth $1000 more and she has $1000 less in cash. Let’s take a look at the accounting equation to illustrate the double entry system. Here is the equation with examples of how debits and credit affect all of the accounts.
With a double-entry system, credits are offset by debits in a general ledger or T-account. The purchase of $5,000 in Fixed Asset equipment appears in both the Cash account and Fixed Asset account since the transaction affects both of the accounts in double-entry accounting. Most accounting software automatically performs double-entry accounting behind the scenes.
In accounting, a debit refers to an entry on the left side of an account ledger, and credit refers to an entry on the right side of an account ledger. To be in balance, the total of debits and credits for a transaction must be equal. Debits do not always equate to increases, and credits do not always equate to decreases. Accounting software automates the process so you don’t have to think about ledgers or T accounts. You simply use the software for your day-to-day invoicing and payments and connect your bank to import expenses directly.
Debits are typically noted on the left side of the ledger, while credits are typically noted on the right side. Double-entry bookkeeping was developed in the mercantile period of Europe to help rationalize commercial transactions and make trade more efficient. It also helped merchants and bankers understand their costs and profits. Some thinkers have argued that double-entry accounting was a key calculative technology responsible for the birth of capitalism. Debit balances should always equal credit balances in a double-entry system. But first, to understand how the double-entry system works, you need to understand the basic accounting equation.

